Setting the Certificates as Default Certificates
Scenario: For establishing a secured communication between remote or local clients (Installed/Windows/Web App) and the Desigo CC Server system, and to secure the web sites and web application, you want to set the certificates (SMC-created or commercial) as default.
This workflow describes the steps for setting the SMC-created Windows-store based (root, host and self-signed) certificates as the default certificates.
For working with commercial certificates you can directly go to step 4 and proceed further.
Reference: For background information, see the reference section.
Workflow diagram:
Prerequisites:
- You have launched SMC.
- The commercial certificates:
- are available at a known location on the disk of the computer where you want to launch the clients (Installed/Web/Windows App).
- (root of the host or self-signed used during website creation/modification) are imported in the appropriate Windows-store using Microsoft Management Console (MMC 3.0) on the non- SMC systems.
- You have cleared the previously set default certificates, if any.
Steps:
- In the SMC tree, select Certificate.
- Click Create Certificate
 and select Create ROOT Certificate (.pfx)
and select Create ROOT Certificate (.pfx)  .
.
- The ROOT Certificate Information expander displays.
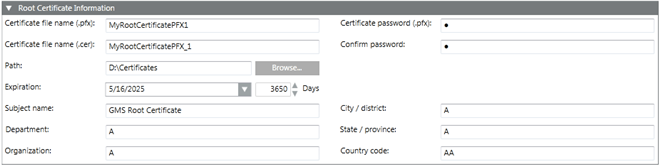
- In the ROOT Certificate Information expander, enter the details as follows:
a. Enter the certificate file name (.pfx).
b. Enter the certificate file name (.cer).
c. Enter the certificate password (.pfx).
d. Click Confirm.
e. Browse for the location to store the root certificate on the disk. By default, the path of the last-created root certificate is selected.
f. Set the Expiration (validity period) duration in days. By default, the certificate expires after 3650 days.
g. Enter the information as required.
— Subject name: (default) GMS Root Certificate: Enter a unique subject name for identifying the root certificate after import in the Issued To field of the Windows Certificate store.
NOTE: It is recommended not to set the subject name as the full computer name. This is because it is required to set the host certificate's subject name as the full computer name and the host and root certificate's subject name cannot be same; otherwise, the client or server communication does not work.
— Department
— Organization
— City/district
— State/province
— Country code (only two characters)
- Click Save
 .
.
- The data is validated, and on successful root certificate creation, two new root certificate files, one with a .pfx extension and the other with a .cer extension, are created at the specified location on the disk.
The root certificate (.pfx file) and its password are used for creating the host certificate from the root.
The root certificate (.cer file) is used for importing the root certificate in the Windows Certificate store when securing client/server communication.
- You have the root certificate (.pfx file) and its password with which you want to create a host (.pfx) certificate.
- For creating a multi host certificate, you have added the entries for the DNS Name and\or the IP address of the host machine in the V3.ext file located at the path
[installation drive:]\[installation folder]\GMSMainProject\Config.
- Click Create Certificate
 and select Create Host Certificate (.pfx)
and select Create Host Certificate (.pfx)  .
.
- The Host Certificate Information expander displays.
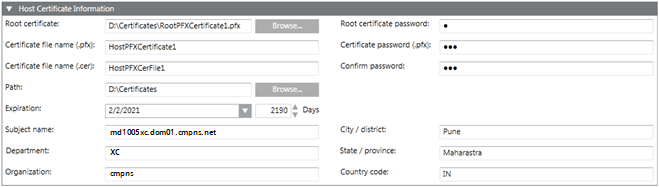
- In the Host Certificate Information expander, enter the details as follows:
a. Browse for the root certificate (.pfx file) from the disk. By default, the last created root certificate (.pfx file) is selected.
b. Enter the root certificate password.
c. Enter the certificate file name (.pfx) of the host certificate.
d. Enter the certificate password (.pfx) for the host certificate and confirm it.
e. Enter the certificate file name (.cer) of the host certificate.
f. Browse for the location to store the certificate on the disk. By default, the path of the last-created root certificate is selected.
g. Set the expiration (validity period) duration in days. By default, the certificate expires after 2190 days.
h. Enter the subject's identifier information as follows:
— Subject name: Change the default to the Full computer name of the host machine where this host certificate will be imported or used, for example, ABCXY022PC.domain01.company.net.
— Department
— Organization
— City/district
— State/province
— Country code (only two characters)
- Click Save
 .
.
- A message displays if the subject name of the host certificate is the same as that of its root certificate.
- Click OK.
- Click Save
 to initiate the file (.pfx).
to initiate the file (.pfx).
- The data is validated and on successful certificate creation, two new host certificate files, one with an extension .pfx and the other with an extension .cer, are created at the specified location on the disk.
The host certificate (.pfx file) is used for importing the host certificate in the Windows Certificate store when securing client/server communication.
You can also use this host certificate (.pfx file) for configuring the CCom port settings for secure web communication. For this, the name of the host certificate must be the full computer name of the Desigo CC server.
- Click Create Certificate
 and select Create Self-Signed Certificate (.pfx)
and select Create Self-Signed Certificate (.pfx)  .
.
- The Self-Signed Certificate Information expander displays.
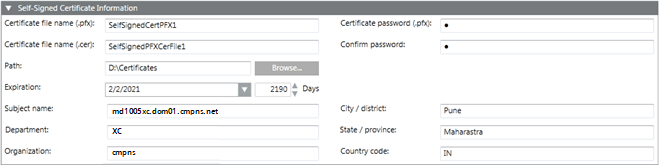
- In the Self-Signed Certificate Information expander, enter the following details:
a. Certificate file name (.pfx).
b. Certificate file name (.cer).
c. Certificate password (.pfx).
d. Click Confirm.
e. Browse for the location to store the self-signed certificate on the disk.
f. Set the expiration (validity period) duration in days. By default, the certificate expires after 2190 days.
g. Enter the following information about the Subject:
— Subject name (default) the Full computer name of the host machine, for example, ABCXY022PC.dom01.company.net. However, you should change this to the full computer name of the host machine, where this self-signed certificate will be imported or used. For example, you can change the default subject name to the full computer name of the host machine where the Web application will be hosted.
NOTE 1: The self-signed certificate is used as the default certificate while creating a Website/application. To create a Website, the certificate that you enter must be the full computer name.
NOTE 2: It is recommended to create only one self-signed certificate with the full computer name. If you create multiple self-signed certificates with the subject name as the full computer name, the Issued to and the Issued by fields of all these multiple certificates will be same and it will be difficult to identify which certificate to use. However, you can identify the certificate using the Thumbprint field of the Details tab, when you view the certificate details.
— Department
— Organization
— City/District
— State/Province
— Country Code (only two characters).
- Click Save
 .
.
- The data is validated, and the two new self-signed certificate files, one with .pfx extension and one with .cer extension, are created at the specified location on the disk.
The self-signed (.pfx file) is used for importing the self-signed certificate in the Windows Certificate store when securing the communication between the server and the remote web server (IIS) using Communication Security expander – Web Server Communication.
 WARNING
WARNING
You should only import certificates obtained from trusted sources. Importing an unreliable certificate could compromise the security of any system component that uses the imported certificate.
- In the SMC tree, select Certificate.
- Click Import Certificate
 .
.
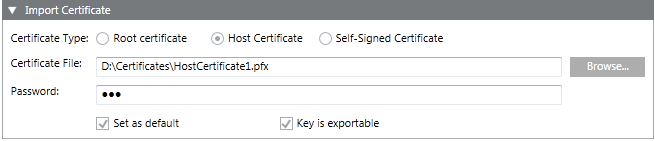
- In the Import Certificate expander, do the following:
a. Select the Certificate type, either Root certificate or Self-signed certificate, to change the default selection Host certificate.
b. Click Browse and select the certificate file. Import the appropriate certificate for the selected Certificate type.
To import the host certificate, you must import the .pfx file of the host certificate.
To import the root certificate, you must import the .cer file of the root .pfx certificate.
To import the self-signed certificate, you must import the .pfx file of the self-signed certificate.
c. Enter the password for the host or self-signed certificate.
d. (Optional) Clear the Set as default check box, if you do not want to set the selected certificate as default. By default, it is selected, if the selected certificate type is not already set as default.
e. (Optional and available only for Host and Self-Signed Certificates) Clear the Key is exportable check box if you do not want to back up or transport your keys at a later time.
NOTE: The key of the certificate used while creating a web application and Client or Server communication (host certificate) must be exportable.
- Click Save
 .
.
- A message displays if the host certificate you are about to import has the same Subject name as that of its root certificate. It is recommended to select a valid host certificate.
- A message displays if the host or root certificate that you are about to import is a CNG certificate with a ECDSA signature algorithm.
- Click OK to import or click Cancel to cancel the dialog box and select another certificate.
- The selected certificate is imported successfully in the certificate store.
The Certificate Type - Root Certificate is imported in Local machine Certificates and User Certificates > Trusted Root Certificate Authorities.
The Certificate Type - Host Certificate is imported in Local machine certificates > Personal.
The Certificate Type - Self-Signed Certificate is imported in Local machine certificates and User Certificates > Trusted Root Certificate Authorities, and in the store Local machine certificates > Personal.
Only the root, host, and self-signed certificates that you have imported in the Windows Certificate store are listed in the Select Certificate dialog box when setting them as default.
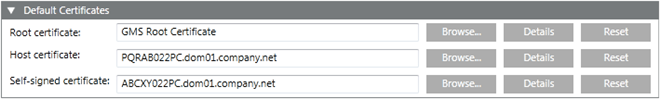
- In the SMC tree, select Certificate.
- The Certificates tab with the Default Certificates expander displays.
- Click Edit
 .
.
- In the Default Certificates expander, do the following:
- Click Browse to open the Select Certificate dialog box.
a. Select a root certificate from the Local machine certificates store location of the Trusted Root Certification Authorities tab.
b. Click OK to close the Select Certificate dialog box. It is recommended to verify the certificate details, by clicking Details.
- Click Browse to open the Select Certificate dialog box.
a. Select a host certificate from the Local machine certificates store location of the Personal tab.
b. Click OK to close the Select Certificate dialog box. It is recommended to verify the certificate details, by clicking Details.
- Click Browse to open the Select Certificate dialog box.
a. Select a self-signed certificate from the Local machine certificates store location of the Personal tab.
b. Click OK to close the Select Certificate dialog box. It is recommended to verify the certificate details, by clicking Details.
- Click Save
 .
.
- If the selected certificate is a CNG certificate with a ECDSA signature algorithm then a message displays informing you that you cannot set this certificate (root or host) as default.
- Click OK and select another certificate.
- The default root, host and self-signed certificates are set.
You may verify the default set certificates in various SMC workflows:
The default root and host certificate display, during project modification on the server and during project creation and modification on the client/FEP, if the client or server communication mode is set asSecured.
The default host certificate displays, during project creation/editing, when the web communication is set asSecured.
The default self-signed certificate displays, during web site and web application creation.