Migrate from SX Open to the Management Platform
Scenario: Integrating OPC data points without the existing Gateway SX Open. The current OPC Excel worksheet is required to process.
Reference: For background information, see the reference section.
Workflow diagram:
Prerequisites:
- The OPC DA Discovery and Scripts extension modules are installed and assigned to the project.
- The following applies to all steps performed in Desigo CC:
- System Manager is in Engineering mode.
- The System Browser is in Management View.

To speed configuration, make sure the Desigo CC Transaction Mode is set to Simple or the Automatic Switch of Transaction Mode is set to True.
The automatic switch setting is recommended. Without it, to re-enable the logs, you need to set the Transaction Mode to Logging at the end of the configuration procedure.
Steps:
- In Excel, open the SX Open configuration file for the current project.
- In Excel, open file OPC_ ConfigurationData_Ver1_1.csv in folder [Installation Drive]:\[Installation Folder]\GMSMainProject\Profiles\OPCDataTemplate.
- Convert the information as per the following table:
a. Proceed in the table line-by-line from top to bottom.
b. First, perform the steps in the column From SX Open file.
c. Perform the steps for the same line in the column To OPC file.
d. Select the Configuration tab if no tab is indicated in the column From SX Open file.
Defining General Information | ||
From SX Open file | To OPC file | Comments |
|
| Only Individual arrays are supported in Desigo CC. Existing alarms in tab BSTR_Hash are not supported. Desigo CC kann zusammengehörige OPC Datenpunktinformation (z.B: Wert, Limite Hoch) auf einen einzelnen BACnet Datenpunkt abbilden. |
|
| In the event a value is entered in the SX Open file, in column C [Computer Name], it must be prefixed by a forward slash (/) in the Prog ID, for example: |
|
| The information in column B [Name] must match section [ITEMS], column A [Parent Group Name]. |
Creating Data Points | ||
From SX Open file | To OPC file | Comments |
|
Example | Data points with a high or low limit must be unique. Supplement the information with a suffix _PrVal, _LoLim, and _HiLim to ensure uniqueness. |
|
Example |
|
|
|
|
No steps. |
| Enter the same description on all data points for the same device. |
Configuring data points | ||
From SX Open file | To OPC file | Comments |
|
| Define the input and output: BACnet = I OPC = IO Two way = IO |
|
| Data type is based on the import rules for library Global_OPC_HQ_1. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
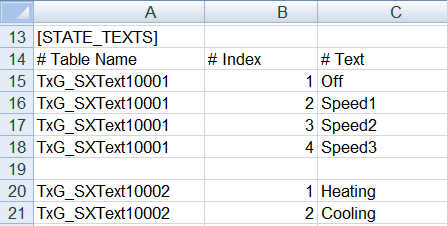
Defining Units and Texts | ||
From SX Open file | To OPC file | Comments |
|
| You must enter a number as the unit, for example: 48 = kW. |
|
| Enter only states that are not standard OPC texts. A separator must be added between the states. |
|
| Example Configuration tab:
Example State tab:
Example result:
The text groups must be manually created in the system. |
Defining Alarm Response | ||
From SX Open file | To OPC file | Comments |
|
| Multiple alarms must be separated by $. Example: |
|
| Example: |
|
| The number of entries in the Alarm class (Syntax, see Notification Class) must match the number of entries in the column Alarm Value. Alarm types: |
|
| The number of entries in the Alarm class and Normal Text) must match the number of entries in the column Alarm Value. Alarm type operators |
|
| The number of entries in the Alarm class and Normal Text) must match the number of entries in the column Alarm Value. NOTE: SX Open could only support one text. |
Creating Data Point Hierarchy | ||
From SX Open file | To OPC file | Comments |
|
Example | Hierarchies are only possible is the information in column L is structured hierarchically. |
Create an OPC Driver
- Select one of the following options, based on where you intend to add the OPC driver:
- Project > Management Station > Servers > Main Server > Drivers
- Project > Management Station > FEPs > [FEP station] > Drivers
- The Object Configurator is displayed.
- Click New object
 and select OPC Client Driver.
and select OPC Client Driver.
- In the New object dialog box, enter the description.
- Click OK.
- The OPC driver object is displayed in System Browser.
Start an OPC Driver
- Select the created driver.
- Click the Extended Operation tab.
- Click, next to the property Manager status, the option Start.
- The status changes to
Start successful.
Create OPC Network
- Select Project > Field Networks
- Click New object
 and select OPC network.
and select OPC network.
- In the New object dialog box, enter the name and description.
NOTE: The description must be unique.
- Click OK.
- The new field network is available in the System Browser.
- Click the OPC tab and open the Network Settings expander.
- Select the OPC driver in the Selected Driver drop-down list.
- Click Save
 .
.
Create the Logical View
- The Logical View has not yet been created.
- System Manager is in Engineering mode.
- In System Browser, select Management View.
- Select Project > System Settings > Views.
- Select the Views tab.
- Enter the data in the following fields:
a. Display name: Logical view
b. Display description: Logical view
c. Base object name: Logical
d. Base object description: Logical
e. Type: Select logical
f. Select distribution: Select check box
g. Supplemental information: (Optional) Enter descriptive text
- Click Save
 .
.
Import the Project Data Files
- One or more valid database files are available locally or by browsing for the reachable network file.
- Select Project > Management station > Servers > Main Server > Drivers.
- In the Extended Operation tab, select the Transaction Mode property.
a. In the drop-down list, select Simple.
b. Click Apply.
NOTE: The Simple option reduces import time, since not all import transactions are written to the project log database. Following engineering, the project must be reset to Logging.
- Select Project > Subsystem Networks > [Network name] and click the Import tab.
- The Import page displays.
- Open the Hierarchies Mapping expander.
- In System Browser, select logical view.
- Drag the top node Logical to the Hierarchies expander, to the Logical line in the column Import hierarchy under this node.
- Click Open at the top of the page to go to the database files.
- In the File type drop-down list, select the data type *.csv.
- Select the desired import files. [*].csv.
- Click Open.
- The preprocessor analyzes the selected file. Click Log Analysis for additional information in the event of a problem.
- In the Source column, select
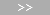 .
.
NOTE: If Delete unselected items from the views is selected, all automation stations and the linked objects are deleted that are not in the selected import file. The main nodes must be manually deleted in the Logical View and User View.
- Click Import.
- The import procedure starts with the first file in the Items to Import list. The State can be:
Completed,Failed,In progress (%),Partially completed[numbers of failed instances].
- A message is displayed at the end of the import process that summarizes the results in a detailed log. Click Import log.
NOTE: The import is not executed if the number of data points exceeds system limits. Check the Number of data points entered in project size.
- Select Project > Management station > Servers > Main Server > Drivers.
- In the Extended Operation tab, select the Transaction Mode property.
a. In the drop-down list, select Logging.
b. Click Apply.

NOTE:
You must reimport if you change the driver configuration after an import.
Read the information in Desigo PX and Desigo TRA for BACnet integration.
Virtual data points must be created, for example, when an average is calculated from two OPC data points. The virtual can be added, for example, for display to the graphic.
- In System Browser, select Application View.
- Select Applications > Logics > Virtual Objects.
- Select the Object Configurator tab.
- Click New Object
 and select the corresponding data type.
and select the corresponding data type.
- In the New Object dialog box, enter the name and description.
- Click OK.
- Click Save
 .
.
For general information on how to create a script, see Step-by-step > Configuring a Project > Configuration Workflows & Procedures > Configuring Scripts.
Copy an Example from the Library
- Select Project > System Settings > Libraries > L1-Headquarters > BA > Software > Desigo Gateway Functionality Scripts > Scripts.
- Select the Script Editor tab.
- The example scripts SXOpenMainScript, SXOpenFunction, SXOpenParser are displayed.
- Select the SXOpenMainScript.
- Open the Viewer expander.
- Select the Script Editor tab.
- Press CTRL+A to highlight all the content and CTRL+C to copy it.
Create and Save a Script
- A new folder is created to save the SX Open Script.
- In System Browser, select Application View.
- Select Applications > Logics > Scripts.
- Select the Script Editor tab.
- Open the Editor expander.
- Delete the default entries.
- Press CTRL+V to paste content.
- Click Save As
 .
.
- In the Save object as dialog box, enter the name and description.
- Click OK.
When Does the Script Path Need to be Changed
The script path must be changed if the Scripts SXOpenFunction and SXOpenParser are modified for a project. The variable ConsoleOutput=true displays the results in the Console expander.

Apply SXAdd Function with COV
The examples in the library were created for the communications from OPC to BACnet. The value (3) in Present_Value must be changed for communications from BACnet to OPC.

- The script is opened in System Manager in the Editor expander.
- In System Browser, select Logical View.
- In the Editor expander, select the predefined function SXAvg and copy the template to the script.
Data Points Configuration
- Enter a unique subscription number (1) as a description.
- Drag the OPC data point from System Manager to the first subscription (2).
- (Optional) Another property can be defined instead of the default property Value (3).
- Enter the function using the corresponding description number (4). This number must be unique throughout the script. The Script editor does not check the numbers for uniqueness.
- Do not change the entry false (5).
- Drag the BACnet data point from System Manager to the first subscription (6).
NOTE: A virtual data point can be assigned instead of a BACnet data point.
- Enter the calculation function (7) SXAdd.
- Enter an offset (8) to the data point value.
Edit Additional Data Points
- Create another SXAdd subscription or select a new script function.
- Repeat the steps as described in Data Points Configuration.
- Deleted unneeded functions from the script.
Apply SXAvg Function with COV
The description is based on three OPC data points.
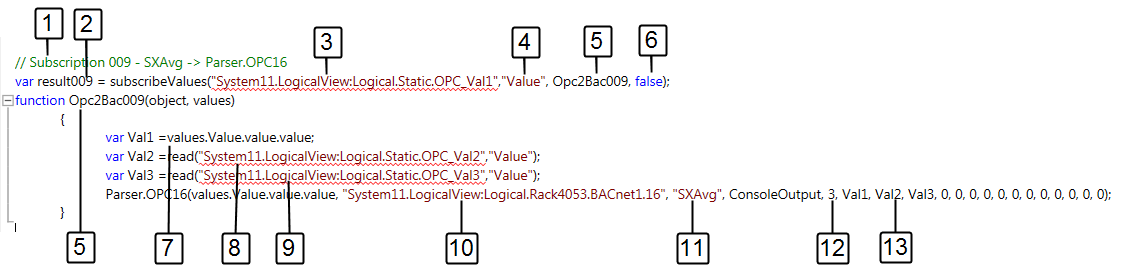
- The preconditions are described in SXAdd.
- In the Editor expander, select the predefined function SXAvg and copy the template to the script.
- Enter a unique subscription number (1) as a description.
- Enter a unique function number (2).
- Drag the OPC data point from System Manager to the first subscription (3).
- (Optional) Another property can be defined instead of the default property Value (4).
- Enter the function using the corresponding description number (5). This number must be unique throughout the script. The Script editor does not check the numbers for uniqueness.
- Do not change the entry false (6).
- In variable 1, enter the parameter (7) for the subscription data point (3).
- Drag the OPC data point from System Manager to the second variable (8).
- Drag the OPC data point from System Manager to the third variable (9).
- Drag the BACnet data point from System Manager to the first subscription (10).
NOTE: A virtual data point can be assigned instead of a BACnet data point.
- Enter the calculation function (11) SXAvg.
- Enter the number (12) of data point values for calculation.
- The number of assigned data point variables (13) must match the numbers of variables (12). The remaining variable must be set to 0.

NOTE:
The average is only calculated if the value of the first subscription changes. Use the polling function to perform continuous averaging.
Apply the SXBetween Function with Polling
The examples in the library were created for communications from OPC to BACnet. The value (4) in Present_Value must be changed for communications from BACnet to OPC.

- The preconditions are described in SXAdd.
- In the Editor expander, select the predefined function SXBetween and copy the template to the script.
- Enter a unique function name (1) as a description. The function name must be unique throughout the script.
- Enter the polling rate (2) in milliseconds. All data points assigned to this function are polled at the same polling rate.
- Drag the OPC data point from System Manager to the first read line (3).
- (Optional) Another property can be defined instead of the default property Value (4).
- Drag the BACnet data point from System Manager to the first read line (5).
- Enter the calculation function (6) SXBetween.
- Enter the minimum and maximum limit value (7) of the data point value for calculation.
- Create additional data points (lines 2 to 4) in this function or create a new function with a different polling rate.
Start and Test the Script
- Click Start
 .
.
- Open the Console expander.
- Check the outputted values.
The OPC import data does not automatically generate system functions (schedulers, or trends). They must be manually created after a data import, based on the most current project SX Open configuration file, if:
- Entries are available in the Schedules tab;
- Entries are available in the Trend tab;
- Entries are available in the Configuration tab (the BACnet alarm info column). They must be checked.
Create Management Station Event for OPC Devices
- You imported a CSV file.
- Select Project > Subsystem networks > [OPC network].
- Select the data point to configure the management station event.
- The alarm details are displayed in the Alarm configuration expander in the Configurator tab.
Additional information on creating events is available in Step-by-step > Configuring a Project > Configuration Workflows & Procedures > Configuring Objects:
- Creating a Discrete Alarm
- Creating a Continuous Alarm
- Creating a BitString Alarm
Create a Scheduler Program
Scenario: You want to create a weekly schedule for an OPC object. The times used in the example must be synchronized against the actual project times.
- You imported a CSV file.
- The number of schedules to be created is based on existing schedule available in the Excel worksheet in the Schedules tab.
- In System Browser, select Application View.
- Select Applications > Schedules.
- The Schedules tab displays.
Create a New Schedule
- Click New
 .
.
- Click New Management Station Schedule.
- In the Schedules section, click the Linked Objects tab.
- In System Browser, select the Manual navigation check box.
- Select Logical View.
- Select Logical View > [Network Name] > [Plant Name] > [Data Point].
- Drag the data point to the Linked Objects section.
- Click the Schedule entries tab and in the Expander under Output values, set the operating mode values for Inactive and Active as follows:
Active=On and Inactive=Off.
- You can now configure the weekly schedule by setting the daily times for each day of the week for Inactive and Active. Each weekday is initially set in full to inactive (Off).
Create Schedule Entries
- In the weekly view to the right, click the column Monday in the Schedule entries tag. The entire is initially set to Inactive.
- Right-click in the Monday column and select Add Weekly Entry. Drag the edge of the entry to set the start time to 8 am and the end time to 5 pm.
- In the Schedule entries tab, select, next to the start time (8:00:00), the change to Active and, next to the end time (17:00:00), the change to Inactive. The timespan from 8 am to 5 pm is now set to Active.
- Repeat steps 2-3 for the remaining days of the week: Tuesday, Wednesday, Thursday, and Friday.
- The schedule is now repeated each week. The timespans that you set, for example, for Thursday, is in other words, repeated each Thursday.
Save Schedule
- Click Save
 .
.
- The Save Object As dialog box displays.
- In the Name field, enter the text Plant on weekdays from 8-17.
- Click OK.
- The new schedule object is available in the System Browser under Management Station Schedules. The operating mode Occupancy Status is automatically set for each day of the week based on settings for Active/Inactive.
Create Online Trend
Scenario: You want to create an online trend for an OPC object.
- You imported a CSV file.
- The number of online trend objects for creation is defined in the Excel worksheet in the Trend tab.
- In System Browser, select logical view.
- Select Logical View > [Network Name] > [Plant Name] > [Data Point].
- In the Related Items, the corresponding related objects are displayed under Trend.
- Click New Trend.
- The information on the trend is displayed in the secondary pane.
- Drag
 the selected data point to the trend application.
the selected data point to the trend application.
- Change the Trend View properties.
- Change the series properties.
- Click Save As
 .
.
- A Save Object As dialog box appears.
- Select the desired folder to save the Trend View.
- Type a name and description for the new Trend View.
- Click OK.
- An online trendlog object is created for each data point in Application View > Trends > Online Log Objects.
Additional information on creating trends is available in Working with Trends.